This notebook contains basic demonstration of how to explore and describe dataset with pandas. The basic outcomnes for this include:
- importing python libraries
- Load a data file into pandas
- Examine the size and data types of a dataframe
- Understand the relationship between DataFrame, Series and Index
- Compute aggreate values from a pandas series
- Compute grouped aggregrate values from a pandas dataframe
- Order a data frame
- Join two pandas dataframes for additional context
- Provide numerical descriptions of a distribution
- Visualize the distribution of a variable
Dataset¶
For this notebook, I used the MovieLens 25M Dataset. The Zip file is 250MB, and the files take about 1.2GB uncompressed. A quick documentation for the dataset is available here
Python modules¶
Most useful python functions are in modules. In other to use them, they need to be first imported
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
Reading CSV¶
movies = pd.read_csv('../Data/ml-25m/movies.csv')
movies
| movieId | title | genres | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | Toy Story (1995) | Adventure|Animation|Children|Comedy|Fantasy |
| 1 | 2 | Jumanji (1995) | Adventure|Children|Fantasy |
| 2 | 3 | Grumpier Old Men (1995) | Comedy|Romance |
| 3 | 4 | Waiting to Exhale (1995) | Comedy|Drama|Romance |
| 4 | 5 | Father of the Bride Part II (1995) | Comedy |
| … | … | … | … |
| 62418 | 209157 | We (2018) | Drama |
| 62419 | 209159 | Window of the Soul (2001) | Documentary |
| 62420 | 209163 | Bad Poems (2018) | Comedy|Drama |
| 62421 | 209169 | A Girl Thing (2001) | (no genres listed) |
| 62422 | 209171 | Women of Devil’s Island (1962) | Action|Adventure|Drama |
62423 rows × 3 columns
The DataFrame¶
movies.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> RangeIndex: 62423 entries, 0 to 62422 Data columns (total 3 columns): # Column Non-Null Count Dtype --- ------ -------------- ----- 0 movieId 62423 non-null int64 1 title 62423 non-null object 2 genres 62423 non-null object dtypes: int64(1), object(2) memory usage: 1.4+ MB
- RangeIndex: indexes 0 to n-1
- 3 columns
- 1
int64 - 2
object– these store strings
- 1
- 62423 rows
- Kind of data
- integer moviedID
- string title
- string genres
- The data is about movies
-Each column is a series. It can be accessed like a disctionary
Series¶
- An array with an index
- All columns of the dataFrame share the same index
movies['title']
0 Toy Story (1995)
1 Jumanji (1995)
2 Grumpier Old Men (1995)
3 Waiting to Exhale (1995)
4 Father of the Bride Part II (1995)
...
62418 We (2018)
62419 Window of the Soul (2001)
62420 Bad Poems (2018)
62421 A Girl Thing (2001)
62422 Women of Devil's Island (1962)
Name: title, Length: 62423, dtype: object
# How big is the series?
from turtle import title
print(movies['title'].size)
print(len(movies['title']))
print(movies['title'].shape)
#count count values not including missing values
movies['title'].count()
62423 62423 (62423,)
62423
- .shape returns the array shape as a tuple — the array is one-dimensional with length 25M
- .size returns the series size (length). len(…) is identical.
- .count() counts values, not including missing value
Another DataFrame¶
Let’s load the ratings
ratings = pd.read_csv('../Data/ml-25m/ratings.csv')
ratings.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> RangeIndex: 25000095 entries, 0 to 25000094 Data columns (total 4 columns): # Column Dtype --- ------ ----- 0 userId int64 1 movieId int64 2 rating float64 3 timestamp int64 dtypes: float64(1), int64(3) memory usage: 762.9 MB
- Data has about 25M instances
- Data contains
- userId(int)
- movieId(int)
- rating(float)
- timestamnp(int)
ratings
| userId | movieId | rating | timestamp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 296 | 5.0 | 1147880044 |
| 1 | 1 | 306 | 3.5 | 1147868817 |
| 2 | 1 | 307 | 5.0 | 1147868828 |
| 3 | 1 | 665 | 5.0 | 1147878820 |
| 4 | 1 | 899 | 3.5 | 1147868510 |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| 25000090 | 162541 | 50872 | 4.5 | 1240953372 |
| 25000091 | 162541 | 55768 | 2.5 | 1240951998 |
| 25000092 | 162541 | 56176 | 2.0 | 1240950697 |
| 25000093 | 162541 | 58559 | 4.0 | 1240953434 |
| 25000094 | 162541 | 63876 | 5.0 | 1240952515 |
25000095 rows × 4 columns
Aggregrate Functions¶
An aggregate function combines a series (or array) into a single value:
ratings['rating'].mean()
3.533854451353085
ratings['rating'].sum()
88346697.0
Alternate form – function from numpy
np.sum(ratings['rating'])
88346697.0
Quantiles¶
Let’s see the quantile function
ratings['rating'].quantile(0.25)
3.0
ratings['rating'].quantile(0.75)
4.0
Interesting. 25% of the ratings is 4 or greater
Grouped Aggregrates¶
We can group by a column and compute aggreagrates within the group.
How many ratings per movie?
ratings.groupby('movieId')['rating'].count()
movieId
1 57309
2 24228
3 11804
4 2523
5 11714
...
209157 1
209159 1
209163 1
209169 1
209171 1
Name: rating, Length: 59047, dtype: int64
We can compute multiple aggregates at the same time:
movie_stats = ratings.groupby('movieId')['rating'].agg(['mean', 'count'])
movie_stats
| mean | count | |
|---|---|---|
| movieId | ||
| 1 | 3.893708 | 57309 |
| 2 | 3.251527 | 24228 |
| 3 | 3.142028 | 11804 |
| 4 | 2.853547 | 2523 |
| 5 | 3.058434 | 11714 |
| … | … | … |
| 209157 | 1.500000 | 1 |
| 209159 | 3.000000 | 1 |
| 209163 | 4.500000 | 1 |
| 209169 | 3.000000 | 1 |
| 209171 | 3.000000 | 1 |
59047 rows × 2 columns
Finding Largest¶
We can get the 10 movies with the most ratings and 10 most rated movie
movie_stats.nlargest(10, 'count')
| mean | count | |
|---|---|---|
| movieId | ||
| 356 | 4.048011 | 81491 |
| 318 | 4.413576 | 81482 |
| 296 | 4.188912 | 79672 |
| 593 | 4.151342 | 74127 |
| 2571 | 4.154099 | 72674 |
| 260 | 4.120189 | 68717 |
| 480 | 3.679175 | 64144 |
| 527 | 4.247579 | 60411 |
| 110 | 4.002273 | 59184 |
| 2959 | 4.228311 | 58773 |
movie_stats.nlargest(10, 'mean')
| mean | count | |
|---|---|---|
| movieId | ||
| 27914 | 5.0 | 1 |
| 31945 | 5.0 | 1 |
| 83161 | 5.0 | 1 |
| 86975 | 5.0 | 1 |
| 92783 | 5.0 | 1 |
| 93991 | 5.0 | 1 |
| 95494 | 5.0 | 1 |
| 96799 | 5.0 | 1 |
| 99243 | 5.0 | 1 |
| 103875 | 5.0 | 1 |
Linking Data¶
Data can refer to other data
- Ratings are instances themselves
- But each connects a user to a movie
We can merge the two.
We want to combine our stats with movie info.
- on=’movieId’ says to use the movieId column of the first frame instead of its index.
- Matches values to index in other frame
movie_info = movies.join(movie_stats, on='movieId')
movie_info
| movieId | title | genres | mean | count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | Toy Story (1995) | Adventure|Animation|Children|Comedy|Fantasy | 3.893708 | 57309.0 |
| 1 | 2 | Jumanji (1995) | Adventure|Children|Fantasy | 3.251527 | 24228.0 |
| 2 | 3 | Grumpier Old Men (1995) | Comedy|Romance | 3.142028 | 11804.0 |
| 3 | 4 | Waiting to Exhale (1995) | Comedy|Drama|Romance | 2.853547 | 2523.0 |
| 4 | 5 | Father of the Bride Part II (1995) | Comedy | 3.058434 | 11714.0 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 62418 | 209157 | We (2018) | Drama | 1.500000 | 1.0 |
| 62419 | 209159 | Window of the Soul (2001) | Documentary | 3.000000 | 1.0 |
| 62420 | 209163 | Bad Poems (2018) | Comedy|Drama | 4.500000 | 1.0 |
| 62421 | 209169 | A Girl Thing (2001) | (no genres listed) | 3.000000 | 1.0 |
| 62422 | 209171 | Women of Devil’s Island (1962) | Action|Adventure|Drama | 3.000000 | 1.0 |
62423 rows × 5 columns
movie_info.nlargest(10, 'count')
| movieId | title | genres | mean | count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 351 | 356 | Forrest Gump (1994) | Comedy|Drama|Romance|War | 4.048011 | 81491.0 |
| 314 | 318 | Shawshank Redemption, The (1994) | Crime|Drama | 4.413576 | 81482.0 |
| 292 | 296 | Pulp Fiction (1994) | Comedy|Crime|Drama|Thriller | 4.188912 | 79672.0 |
| 585 | 593 | Silence of the Lambs, The (1991) | Crime|Horror|Thriller | 4.151342 | 74127.0 |
| 2480 | 2571 | Matrix, The (1999) | Action|Sci-Fi|Thriller | 4.154099 | 72674.0 |
| 257 | 260 | Star Wars: Episode IV – A New Hope (1977) | Action|Adventure|Sci-Fi | 4.120189 | 68717.0 |
| 475 | 480 | Jurassic Park (1993) | Action|Adventure|Sci-Fi|Thriller | 3.679175 | 64144.0 |
| 522 | 527 | Schindler’s List (1993) | Drama|War | 4.247579 | 60411.0 |
| 108 | 110 | Braveheart (1995) | Action|Drama|War | 4.002273 | 59184.0 |
| 2867 | 2959 | Fight Club (1999) | Action|Crime|Drama|Thriller | 4.228311 | 58773.0 |
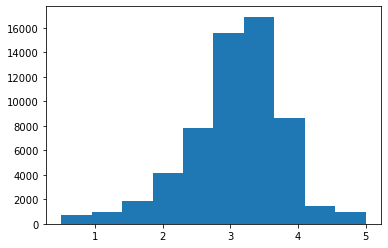
Average Movie Rating¶
let’s look at the distribution of average movie rating:
movie_info['mean'].describe()
count 59047.000000 mean 3.071374 std 0.739840 min 0.500000 25% 2.687500 50% 3.150000 75% 3.500000 max 5.000000 Name: mean, dtype: float64
Let’s make a histogram:
plt.hist(movie_info['mean'])
plt.show()
And with more bins:
plt.hist(movie_info['mean'], bins=50)
plt.show()
Wrapping Up¶
- A dataframe consists of columns
- Each column is a series: array with index
- We can call info() method to quickly see
- how many rows (instances)
- what columns
- data types
- Aggregrates combine a series or array into a single value
- Can compute over a whole series or over groups
- Join combines frames
- data description can be presented numerically and visually