In computer science, an algorithm is a step by step instruction for solving problems. There are broadly two ways to make an algorithm- Pseudocode or flowchart.
Pseudocode is a step by step approach to solve a problem using human readable language. It is an implementation of algorithm using text and annotations written in plain english. Pseudocode as the name suggest is a false code and should be understood by a non-programmer and interpreted by programmers with no matter their programming background.
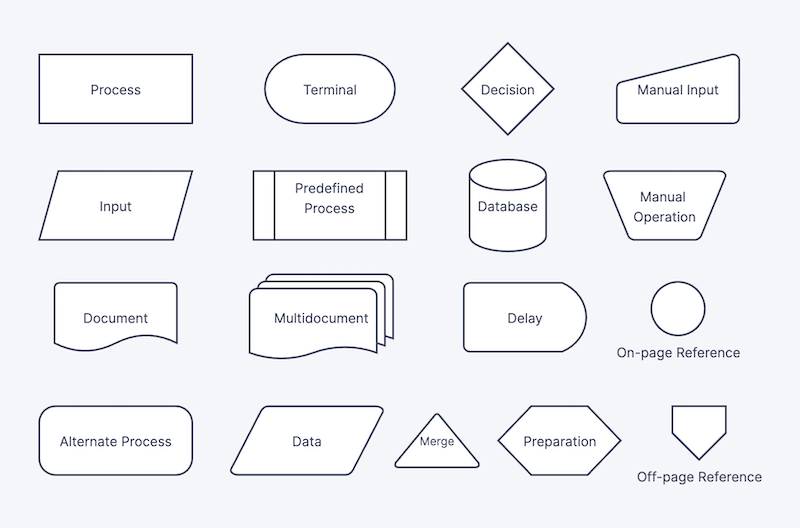
A flowchart is a type of diagram that visually represents a workflow or process using a set of symbols or icons to denote different actions/decisions/steps within the process with arrows showing the direction of the flow. The commonly used flowchart symbols are shown in the figure below:

Let look at some implement of algorithm using 3 simple examples.
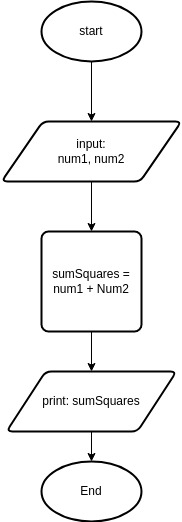
Case 1: Develop an algorithm to calculate the sum of squares of given input of numbers.
num1 = Input (“Enter the first number”)
num2 = Input (“Enter the second number”)
sumSqaures = num1*num1 + num2*num2
Print(sumSquares)

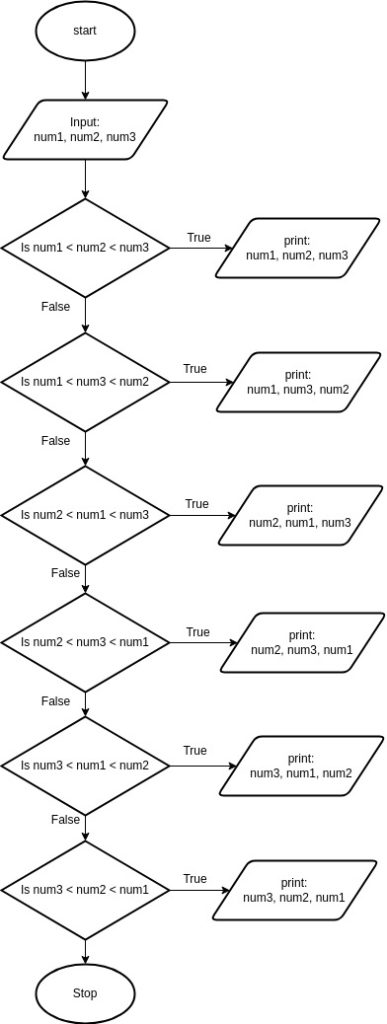
Case 2: Develop an algorithm that reads in three numbers and writes them all in sorted order
num1 = Input (‘Enter the first number’)
num2 = Input (‘Enter the second number’)
num3 = Input (‘Enter the third number’)
If (num1 < num2 < num3)
Print num1 , num2, num3
else If (num1 < num3 < num2)
Print num1 , num2, num3
else If (num2 < num1 < num3)
Print num2 , num1, num3
else If (num2 < num3 < num1)
Print num2 , num3, num1
else If (num3 < num1 < num2)
Print num3 , num1, num2
else If (num3 < num2< num1)
Print num3 , num2, num1

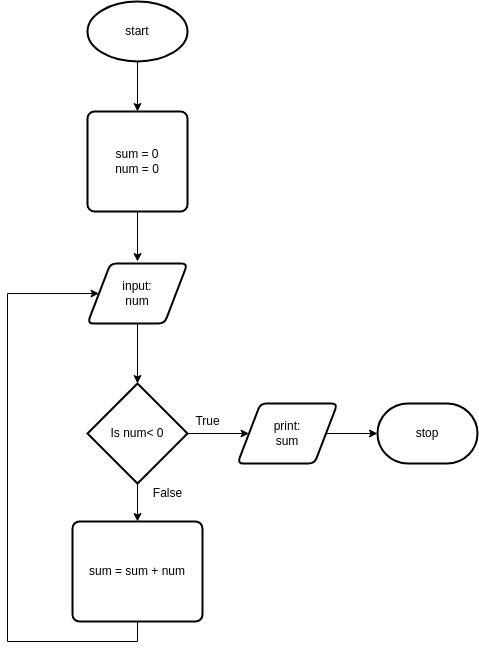
Case 3: Develop an algorithm that calculate a running sum. A user will enter numbers that will be added to the sum and when a negative number is encountered, stop adding numbers and write out the final result
sum = 0
num = 0
While num >= 0:
num = Input(‘Enter the number to add’)
if num >= 0:
sum = sum + num
else:
print(sum)